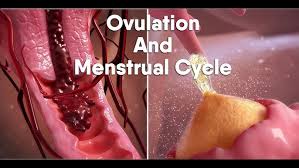
The menstrual cycle is a natural and complex process that occurs in the female body, preparing it for potential pregnancy. While often referred to as “periods” or “ovulation cycles,” this process involves various phases, hormonal changes, and physiological events that allow for the development of a potential pregnancy. Despite its fundamental role in human reproduction, many individuals remain unaware of the intricate details that govern the menstrual cycle and ovulation. The development of medical animations, such as those produced by DandelionTeam, has made it easier for people to visualize and understand these processes.
This article will explore the key phases of the menstrual cycle, how ovulation works, the hormonal interplay at each stage, and the significance of medical animation in enhancing understanding. By the end, readers will gain a clearer understanding of how their bodies work and the valuable role educational tools like medical animation play in providing clarity.
1. Introduction to the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle refers to the regular changes in hormone levels and the physiological events that prepare a woman’s body for pregnancy. The cycle is typically around 28 days but can range from 21 to 35 days, with variations depending on the individual. The cycle is regulated by a delicate balance of hormones that influence various organs, including the ovaries, uterus, and brain.
The cycle can be divided into several distinct phases, each with its own purpose and physiological events. These phases include:
- Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5)
- Follicular Phase (Days 1-14)
- Ovulation (Day 14)
- Luteal Phase (Days 15-28)
2. The Menstrual Phase: Shedding the Endometrial Lining
The menstrual phase marks the beginning of the cycle. This phase is commonly referred to as the “period” and typically lasts between 3 and 7 days. During this phase, the body sheds the endometrial lining that had built up in anticipation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, the levels of estrogen and progesterone drop, causing the endometrial lining to break down and be expelled from the body through the vagina.
During the menstrual phase, medical animation plays a crucial role in illustrating the physical changes that occur, such as the shedding of the uterine lining. By using visualizations, medical animations allow for a deeper understanding of how hormones and bodily structures interact during this phase.
3. The Follicular Phase: Preparing for Ovulation
The follicular phase begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts until ovulation, typically around day 14 of a 28-day cycle. During this phase, the pituitary gland secretes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles. Each follicle contains an immature egg, and usually, one follicle will become dominant and mature into an egg, while the others will gradually disappear.
As the follicle matures, it produces estrogen, which thickens the endometrial lining in preparation for the implantation of a fertilized egg. Medical animations can help illustrate how estrogen influences the maturation of the follicle and the changes that occur in the uterus, offering viewers a comprehensive understanding of the follicular phase’s role in fertility.
4. Ovulation: The Release of the Egg
Ovulation is the process by which a mature egg is released from the ovary. This typically occurs around day 14 in a 28-day cycle, triggered by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH), which works in tandem with FSH. The egg then travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus, where it may encounter sperm for fertilization.
Medical animations depicting ovulation help to show the complexity of the process, including the role of LH and FSH in triggering egg release, the passage of the egg through the fallopian tube, and the timing required for fertilization to occur. By visualizing these processes, viewers gain an understanding of how ovulation is central to conception and why timing matters for those trying to conceive.
5. The Luteal Phase: Preparing for Pregnancy
After ovulation, the luteal phase begins. The ruptured follicle transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone. This hormone is responsible for further thickening the endometrial lining to create an optimal environment for a fertilized egg to implant.
If fertilization occurs, the embryo will implant into the thickened uterine lining, and the body will begin producing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which maintains the corpus luteum and prevents menstruation. If no fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum degenerates, causing progesterone levels to fall. This drop in progesterone triggers the shedding of the endometrial lining, leading to the start of a new menstrual cycle.
Medical animations of the luteal phase are incredibly helpful in showing how hormonal changes during this phase directly influence the uterus, the ovaries, and the potential for pregnancy. They highlight the role of progesterone and the relationship between the corpus luteum, endometrial lining, and fertilization.
6. Hormonal Regulation and its Impact on the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is regulated by a sophisticated interplay of hormones, primarily estrogen, progesterone, LH, and FSH. These hormones are produced by the ovaries, pituitary gland, and hypothalamus, each of which plays a key role in the cycle’s progression.
- Estrogen: Primarily responsible for stimulating the growth of the uterine lining and the maturation of eggs in the follicles.
- Progesterone: Prepares the endometrium for pregnancy and regulates the menstrual cycle after ovulation.
- FSH: Stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles.
- LH: Triggers ovulation by causing the mature follicle to release an egg.
Each of these hormones is at different levels during each phase of the menstrual cycle. Medical animations can illustrate these fluctuating hormone levels and their impact on the reproductive organs, helping users grasp the significance of hormone balance in fertility and overall reproductive health.
7. The Role of Medical Animation in Understanding the Menstrual Cycle
Medical animation has become an invaluable tool for visualizing and educating the public about the menstrual cycle and its related processes. These animations provide detailed, accurate, and easily understandable representations of complex biological systems. The power of visual learning allows people to see the physiological changes that occur in the body, making abstract concepts more tangible.
For example, DandelionTeam’s medical animations can help explain the precise mechanisms of hormone secretion, the process of ovulation, the role of the corpus luteum, and much more. By incorporating color, motion, and 3D models, these animations provide an engaging way to learn about a subject that is often considered difficult to understand without visuals.
8. Addressing Common Misconceptions and Myths
There are many myths surrounding the menstrual cycle and ovulation. For example, many people mistakenly believe that ovulation occurs exactly on day 14 of the cycle, which is not always the case. Variations in cycle length, stress, illness, and other factors can all influence ovulation timing.
Additionally, some may think that menstrual cycles are always regular and predictable, but this is not true for everyone. Understanding the flexibility of the menstrual cycle and the factors that influence it is critical for individuals who are trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy. Medical animations can clarify these points by showing how each phase of the cycle can vary from person to person.
9. The Importance of Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle
Understanding the menstrual cycle is vital for several reasons. First, it empowers individuals to take charge of their reproductive health, whether they are trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy. Second, knowing the signs of ovulation and the hormonal changes during each phase of the cycle can help people identify potential health issues, such as hormonal imbalances, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or thyroid problems.
By using medical animation tools like those offered by DandelionTeam, individuals can better understand the functions of their bodies, spot irregularities, and make informed decisions about their health.
10. Conclusion
The menstrual cycle is a remarkable process, with each phase playing a critical role in reproductive health. By understanding the hormonal interplay and physiological changes that occur during the cycle, individuals can gain better insights into their bodies and fertility.
Medical animations, such as those created by DandelionTeam, have revolutionized the way we learn about and visualize these processes. These animations not only enhance education but also help to demystify a natural process that affects millions of people worldwide. By making complex biology easier to understand, medical animations foster greater awareness, which ultimately leads to better health outcomes for individuals.
As we continue to explore the complexities of the menstrual cycle and ovulation, tools like medical animation will play a crucial role in enhancing our understanding and improving access to education about reproductive health. Whether for personal knowledge or medical practice, these visual tools are essential in making biology more accessible and comprehensible to all.
This comprehensive exploration of the menstrual cycle and ovulation, paired with the power of medical animation, provides a unique resource for individuals seeking a deeper understanding of their bodies. By leveraging visual and educational tools, we can ensure that this crucial aspect of human biology is better understood and appreciated.